Looking at my Raspberry Pi Zero and maybe being partially inspired by the now defunct "One Laptop Per Child" project from a few years ago, which aimed at building a laptop for under $100, I wondered if a usable computer could be created out of the Raspberry Pi Zero. Or maybe it's just the challenge of seeing how far this tiny computer can be pushed that had me wondering whether this was even possible. Is there much point to this? Probably not. However, even though this may not be that practical, the Pi Zero, could be replaced with the slightly more expensive Pi 4 2GB, which would make for a pretty efficient and usable desktop PC.
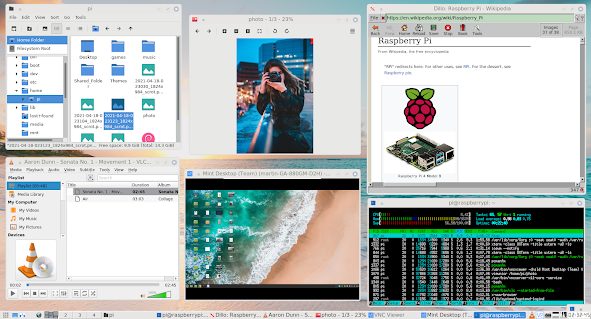 |
| A complete set of desktop apps including file browser, media player, browser and remote desktop running in 130MB RAM. |
What is a Raspberry Pi Zero..? It's a single board computer built by the Raspberry Pi Foundation which can easily fit in the palm of your hand being just 65mm x 30mm. There are basically two different Pi Zero models, which are differentiated by having WIFI and Bluetooth or not. (There's also the more recently launched Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W, which has 4 cores, but the same 512 MB RAM and the form factor.) Costing just over $10 for the WIFI + Bluetooth model, they are very affordable and might just make for a very cheap base to build a computer. Another interesting point is that they are so energy efficient that they can be powered from a battery pack for hours or even from solar panels. That being said however, it was not designed to be a desktop computer as it's mostly used as an embedded device in robotics, sensor reading or computer vision projects. For a more powerful desktop machine, there is the current latest version, the Pi 4, which actually makes for a pretty usable machine, but at a higher cost.
I suppose to some degree, the goals of the Pi Foundation aligns partially with the OLPC initiative in that their goal is around education. It seems to be a perfect fit - if the hardware could be pushed beyond what it was designed for.
So, how could a simple £10 board be converted into a PC? For starters, the board comes bare, in that there are no peripherals.
For that, we're going to have to add a few parts:1) Keyboard
2) Mouse
3) Monitor
4) SD Card
5) Case
6) Power Supply
7) Mini HDMI to HDMJI adapter
8) Micro USB to USB adapter
9) Depending on whether HDMI sound is used or not, a USB hub and sound card
The most expensive part of the build will probably be the monitor, but if a cheap monitor is used, it may still come in at around $100.
With the hardware defined, the next part is the software. This is arguably the most important part. We're going to be running a Linux distribution on the computer. The Raspberry Pi Foundation has done some excellent work on packaging a Linux based operating system for the the Raspberry Pi. However, I suspect that the desktop version of their OS is more aimed at the much more powerfull Raspberry Pi 4 and not the Zero. Thus, whilst it technically works on the Pi Zero, to me, it's too slow. The Pi Zero has very limited specs, the highlights being:
- 1GHz ARM CPU - BCM 2835 SOC
- 512MB RAM
- Wifi and Bluetooth
- Insert the SD card into an card reader and insert into a PC.
- Download Raspberry Pi OS Lite from https://www.raspberrypi.org/software/operating-systems/#raspberry-pi-os-32-bit
- Write the Image file to the SD card - Depending on the whether Mac, Windows or Linux is used, there are slightly different steps involved, but there are many guides online as to how to do this.
- Insert the card into the Raspberry Pi, plug in the accessories and boot the device. At this point, the device should boot into the command line interface, requesting a login.
- Login with the account "Pi" and the password "raspberry"
- Type in sudo raspi-config
- Setup the wifi connection.
- Enable SSH for remote management using the command prompt
- Enable realvnc for remote management using a remote desktop connection
- Change the default password
- Exit the config tool and execute the following commands:
- sudo apt update
- sudo apt upgrade
- sudo apt install icewm
- sudo apt install --no-install-recommends xserver-xorg
- sudo apt install lightdm
- sudo reboot
- At this point, it should boot into the desktop user interface. Click on the start menu and click on Terminal
- Type in the following commands into the terminal
- sudo apt install xarchiver
- sudo apt install leafpad
- sudo apt install pcmanfm
- sudo apt install dillo
- wget https://www.realvnc.com/download/file/viewer.files/VNC-Viewer-6.20.529-Linux-ARM.deb
- sudo dpkg -i VNC-Viewer-6.20.529-Linux-ARM.deb
- sudo apt install midori
- sudo apt install gimp
- sudo apt install nitrogen
- sudo apt install lxappearance
- sudo apt install vlc
- sudo apt install omxplayer
- sudo apt install ffmpeg
- cd ~ && wget https://github.com/KenT2/tboplayer/tarball/master -O - | tar xz && cd KenT2-tboplayer-* && chmod +x setup.sh && ./setup.sh
- sudo apt install python-tk
- sudo apt install abiword
- sudo apt install viewnior
- sudo apt install gcalculator
- sudo apt install scrot
- sudo apt install synaptic
- sudo apt install pi-package
- sudo apt install wicd
- Download and install the ariata light theme from https://www.box-look.org/p/1321163/
- Download and install the Papirus Icon light theme: wget https://git.io/papirus-icon-theme-install | sh
- Download your prefered background and set with Nitrogen
- Set the Icon theme to Papirus
- Set the IceWM theme to ariata light
| icewm | - The desktop environment |
| lightdm | - Login manager |
| xarchiver | - Compression software |
| leafpad | - Text Editor |
| pcmanfm | - File Explorer |
| dillo | - Web Browser |
| VNC-Viewer | - Remote Desktop Client |
| midori | - Modern Browser |
| gimp | - Image Editor |
| nitrogen | - Desktop Background setting |
| lxappearance | - Desktop settings |
| vlc | - Media Player |
| omxplayer, ffmpeg, tboplayer, python-tk | - Youtube Downloader and player |
| abiword | - Word Processor |
| viewnior | - Image viewer |
| gnome-calculator | - Calculator |
| scrot | - Screenshot software |



0 comments